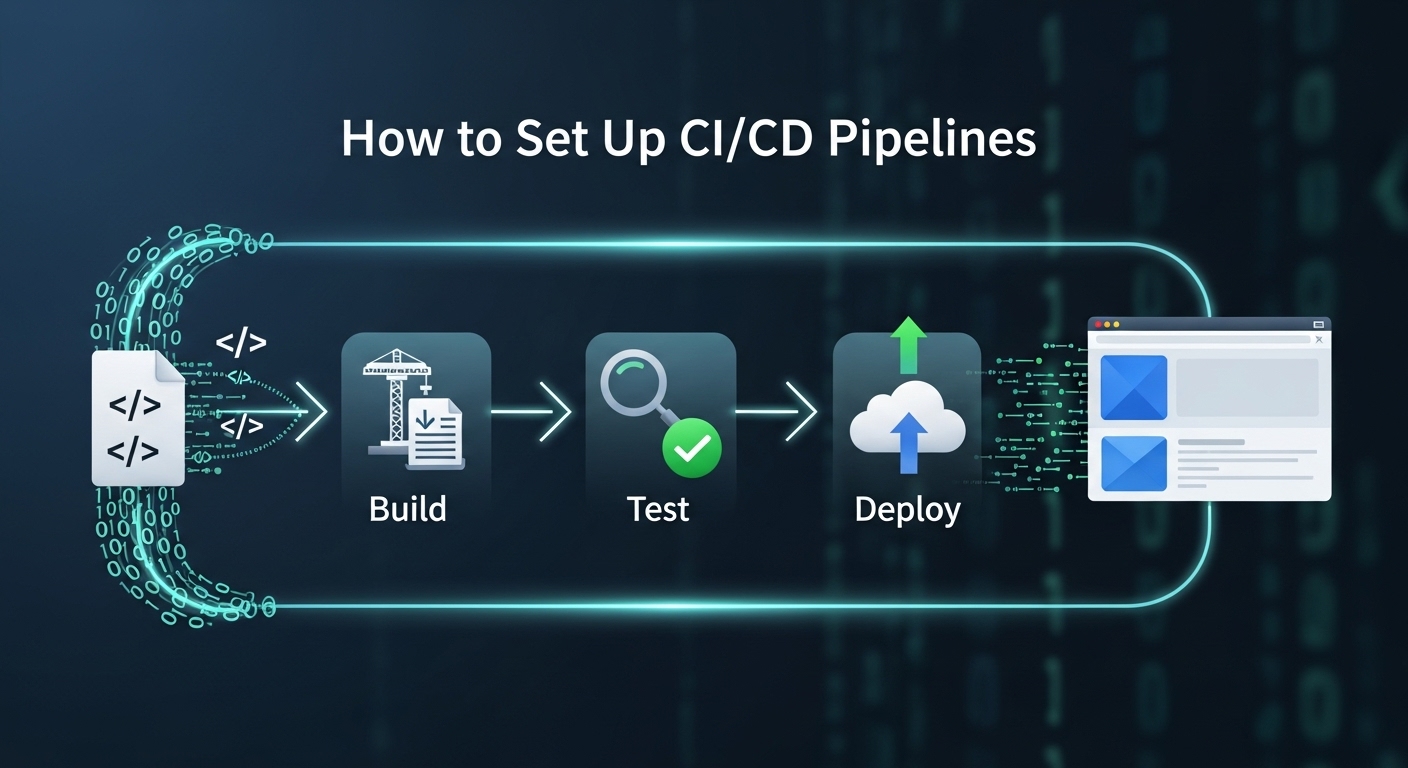
Setting up CI/CD pipelines represents one of the most transformative practices in modern software development. When you implement continuous integration and continuous deployment correctly, you’ll dramatically reduce deployment risks, accelerate release cycles, and improve code quality across your development teams.
But where do you begin? How do you move from manual deployments to fully automated CI/CD pipelines that deliver code seamlessly from development to production?
Let’s explore the essential steps and strategies that will guide you through building robust, efficient CI/CD pipelines for your projects.
Understanding CI/CD Pipelines: The Foundation
Before diving into implementation, what exactly makes a CI/CD pipeline effective? Think about your current development workflow. How much time does your team spend on manual testing, building, and deployment tasks? How often do integration issues surface late in the development cycle?
Continuous Integration (CI) automatically builds, tests, and validates code changes as developers commit them to version control. Continuous Deployment (CD) extends this automation through staging environments all the way to production releases.
Consider this scenario: A developer pushes code changes to your repository. Within minutes, your CI/CD pipeline automatically runs comprehensive tests, builds the application, deploys to staging, and—if all checks pass—releases to production. This automation eliminates human error, reduces deployment anxiety, and enables rapid iteration.
Step 1: Choose Your CI/CD Platform and Tools
Which CI/CD platform aligns best with your team’s needs and infrastructure? The choice significantly impacts your pipeline’s capabilities and maintenance requirements.
Popular CI/CD Platforms:
Platform | Best For | Key Features |
Jenkins | Self-hosted, complex workflows | Extensive plugin ecosystem, full customization |
GitHub Actions | GitHub-integrated projects | Native GitHub integration, marketplace actions |
GitLab CI/CD | GitLab users, DevSecOps | Built-in security scanning, comprehensive toolchain |
CircleCI | Docker-based workflows | Excellent Docker support, parallel execution |
Azure DevOps | Microsoft ecosystem | Tight Azure integration, enterprise features |
What factors should guide your platform selection? Consider your team size, budget, existing toolchain, security requirements, and infrastructure preferences. For teams new to CI/CD pipelines, GitHub Actions or GitLab CI/CD offer gentler learning curves with powerful capabilities.
Step 2: Design Your Pipeline Architecture
How should you structure your CI/CD pipeline for optimal efficiency and reliability? The architecture determines your pipeline’s scalability, maintainability, and performance characteristics.
Essential Pipeline Stages:
- Source Stage: Triggers when code changes reach your repository. Configure webhooks or polling mechanisms to detect commits, pull requests, or tag creation.
- Build Stage: Compiles source code, resolves dependencies, and creates deployable artifacts. This stage should produce consistent, reproducible builds regardless of the execution environment.
- Test Stage: Executes automated test suites including unit tests, integration tests, and end-to-end tests. Parallel test execution significantly reduces pipeline duration.
- Security Stage: Performs security scans, vulnerability assessments, and compliance checks. Tools like SonarQube and Snyk integrate seamlessly into CI/CD pipelines.
- Deploy Stage: Releases validated code to target environments using deployment strategies like blue-green deployments or rolling updates.
What deployment strategy best fits your application requirements? Blue-green deployments minimize downtime but require double infrastructure. Rolling deployments gradually replace instances, maintaining service availability throughout the process.
Step 3: Configure Version Control Integration
How does your pipeline interact with your version control system? Proper integration ensures your CI/CD pipeline responds appropriately to different types of code changes and branching strategies.
- Branch Strategy Configuration: Configure your CI/CD pipeline to handle different branch types appropriately. Feature branches might trigger basic build and test stages, while main branch commits initiate full deployment pipelines.
- Webhook Configuration: Set up webhooks that notify your CI/CD platform about repository events. This enables real-time pipeline triggering without constant polling, reducing resource usage and improving responsiveness.
Consider implementing GitFlow or GitHub Flow branching strategies that align with your CI/CD pipeline design. These workflows provide clear rules about when and how code moves between branches, environments, and ultimately to production.
Step 4: Implement Comprehensive Testing Strategies
What testing approaches ensure your CI/CD pipeline catches issues before they reach production? A robust testing strategy forms the backbone of reliable automated deployments.
Test Pyramid Implementation:
- Unit Tests (Foundation): Fast, isolated tests covering individual functions and components. These should comprise 70-80% of your test suite and execute in seconds.
- Integration Tests (Middle): Verify interactions between components, databases, and external services. These tests catch interface issues that unit tests might miss.
- End-to-End Tests (Top): Simulate complete user workflows through your application. While slower and more brittle, these tests validate critical user journeys.
- Performance and Load Testing: Automated performance tests prevent regressions and ensure your application meets performance requirements under various load conditions.
How do you balance test coverage with pipeline speed? Implement parallel test execution, smart test selection based on code changes, and tiered testing strategies that run comprehensive suites for critical branches while executing targeted tests for feature development.
Step 5: Set Up Environment Management and Infrastructure as Code
How do you ensure consistent environments throughout your deployment pipeline? Environment inconsistencies represent one of the primary sources of deployment failures and production issues.
- Infrastructure as Code (IaC): Define your infrastructure using code with tools like Terraform, AWS CloudFormation, or Azure ARM templates. This approach ensures environment consistency, version control for infrastructure changes, and reproducible deployments.
- Environment Promotion Strategy: Design a clear progression path: Development → Staging → Production. Each environment should mirror production as closely as possible while serving specific validation purposes.
- Configuration Management: Implement centralized configuration management using tools like HashiCorp Vault for secrets or cloud-native solutions like AWS Parameter Store. Separate configuration from code and manage environment-specific settings securely.
Consider containerization with Docker and orchestration platforms like Kubernetes to achieve consistent deployment artifacts across all environments. Containers eliminate “works on my machine” problems and simplify the deployment process.
Step 6: Implement Monitoring, Logging, and Alerting
How do you maintain visibility into your CI/CD pipeline performance and application health? Comprehensive observability enables rapid issue detection and resolution.
- Pipeline Monitoring: Track pipeline success rates, execution times, and failure patterns. Identify bottlenecks and optimization opportunities through detailed metrics collection.
- Application Monitoring: Implement application performance monitoring (APM) tools like New Relic, Datadog, or Prometheus to monitor application health, performance metrics, and user experience indicators.
- Logging Strategy: Centralize log collection and analysis using tools like the ELK Stack (Elasticsearch, Logstash, Kibana) or cloud solutions like AWS CloudWatch. Structured logging improves searchability and analysis capabilities.
- Alerting Configuration: Set up intelligent alerting that notifies relevant team members about pipeline failures, performance degradations, or security issues. Avoid alert fatigue through thoughtful threshold configuration and alert routing.
Step 7: Establish Security and Compliance Integration
How do you embed security practices throughout your CI/CD pipeline without slowing development velocity? Security integration, often called DevSecOps, ensures vulnerabilities are caught early in the development cycle.
Security Scanning Integration:
- Static Application Security Testing (SAST): Analyzes source code for security vulnerabilities, code quality issues, and compliance violations.
- Dynamic Application Security Testing (DAST): Tests running applications for security vulnerabilities, particularly useful for web applications.
- Dependency Scanning: Identifies vulnerabilities in third-party libraries and dependencies using tools like OWASP Dependency Check or Snyk.
- Container Security: Scans container images for vulnerabilities and configuration issues before deployment.
Compliance Automation:
Implement automated compliance checks that verify adherence to organizational policies, industry standards, and regulatory requirements. This includes code quality gates, security policy enforcement, and audit trail generation.
Advanced CI/CD Pipeline Patterns and Best Practices
What patterns enhance CI/CD pipeline reliability and efficiency as your organization scales?
- Feature Flags Integration: Implement feature flags to decouple deployment from release, enabling safer rollouts and rapid feature toggling. Tools like LaunchDarkly or Split integrate seamlessly with CI/CD pipelines.
- Canary Deployments: Gradually roll out changes to a subset of users before full deployment. This pattern enables early issue detection with minimal user impact.
- Pipeline as Code: Version control your pipeline definitions alongside application code. This ensures pipeline changes follow the same review and approval processes as code changes.
- Artifact Management: Implement proper artifact versioning, storage, and retention policies. Tools like Artifactory or Nexus Repository provide enterprise-grade artifact management capabilities.
Common CI/CD Pipeline Challenges and Solutions
What obstacles might you encounter when implementing CI/CD pipelines, and how can you overcome them?
- Challenge: Slow Pipeline Execution Solution: Implement parallel execution, optimize test suites, cache dependencies, and use incremental builds.
- Challenge: Flaky Tests Solution: Identify and fix unstable tests, implement test quarantine processes, and improve test environment consistency.
- Challenge: Complex Branching Strategies Solution: Simplify branching models, implement clear merge policies, and automate branch protection rules.
- Challenge: Security Integration Resistance Solution: Implement security scanning gradually, provide developer training, and integrate security feedback into development workflows.
Measuring CI/CD Pipeline Success
How do you evaluate your CI/CD pipeline effectiveness? Key metrics provide insights into performance, reliability, and business impact.
Key Performance Indicators:
- Deployment Frequency: How often you deploy code to production
- Lead Time: Time from code commit to production deployment
- Change Failure Rate: Percentage of deployments causing production failures
- Mean Time to Recovery: Average time to restore service after failures
These metrics, known as DORA metrics, correlate strongly with organizational performance and software delivery effectiveness.
Getting Started: Your Next Steps
Ready to implement CI/CD pipelines in your organization? Begin with these actionable steps:
- Assess Current State: Evaluate existing development and deployment processes
- Start Small: Implement CI/CD for a single, non-critical application
- Build Team Skills: Invest in training and knowledge sharing
- Iterate and Improve: Continuously refine your pipeline based on feedback and metrics
- Scale Gradually: Expand CI/CD adoption across additional projects and teams
Remember, successful CI/CD implementation is a journey, not a destination. Focus on continuous improvement, team collaboration, and gradual adoption rather than attempting perfect implementation from the start.
CI/CD pipelines transform software development by automating repetitive tasks, reducing errors, and enabling rapid, reliable deployments. By following these guidelines and adapting them to your specific context, you’ll build robust automation that accelerates delivery while maintaining quality and security standards.
What will be your first step in implementing CI/CD pipelines? The most important action is simply to begin—choose a small project, select appropriate tools, and start building your automation capabilities today.